Water Flooding Improved Recovery โดย Junior Roustabout … บทความโดยน้องคนนึงที่ใช้นามแฝงว่า Junior Roustabout ครับ
ใครมีความรู้อะไรอยากแบ่งปันก็ยินดีเป็นสื่อกลางนะครับ ส่งมาที่ nongferndaddy@hotmail.com นะครับ
Water Flooding Improved Recovery
โดย Junior Roustabout
ก่อนเข้าเรื่อง ขออธิบายคำว่า Improved Oil Recovery ก่อน, Improved Oil Recovery คือขั้นตอนการเอาน้ำมันออกมาจากแหล่งกักเก็บ โดยการเพิ่มพลังงานเข้าไปที่แหล่งกักเก็บ เพื่อให้มันรีดน้ำมันออกมาได้เยอะขึ้น
การทำ Improved Oil Recovery หลายวิธี เช่น Water flooding, Polymer flooding, Alkaline flooding โดยการเลือกทำแต่ละวิธีนั้น ขึ้นอยู่กับลักษณะทางกายภาพของแหล่งกักเก็บ และน้ำมันด้วย
ลักษณะทางกายภาพของแหล่งกักเก็บ เช่น Formation type (ชั้นหิน), Net thickness (ความหนาของแหล่งกักเก็บ), Average permeability (อัตราการซึมน้ำได้), depth (ความลึก), temperature (อุณหภูมิ) ลักษณะทางกายภาพของน้ำมัน เช่น API Gravity (ดัชนีบอกน้ำหนักของน้ำมันดิบ), Oil Viscosity (ความหนืด), Composition (ส่วนประกอบทางเคมี), Oil Saturation
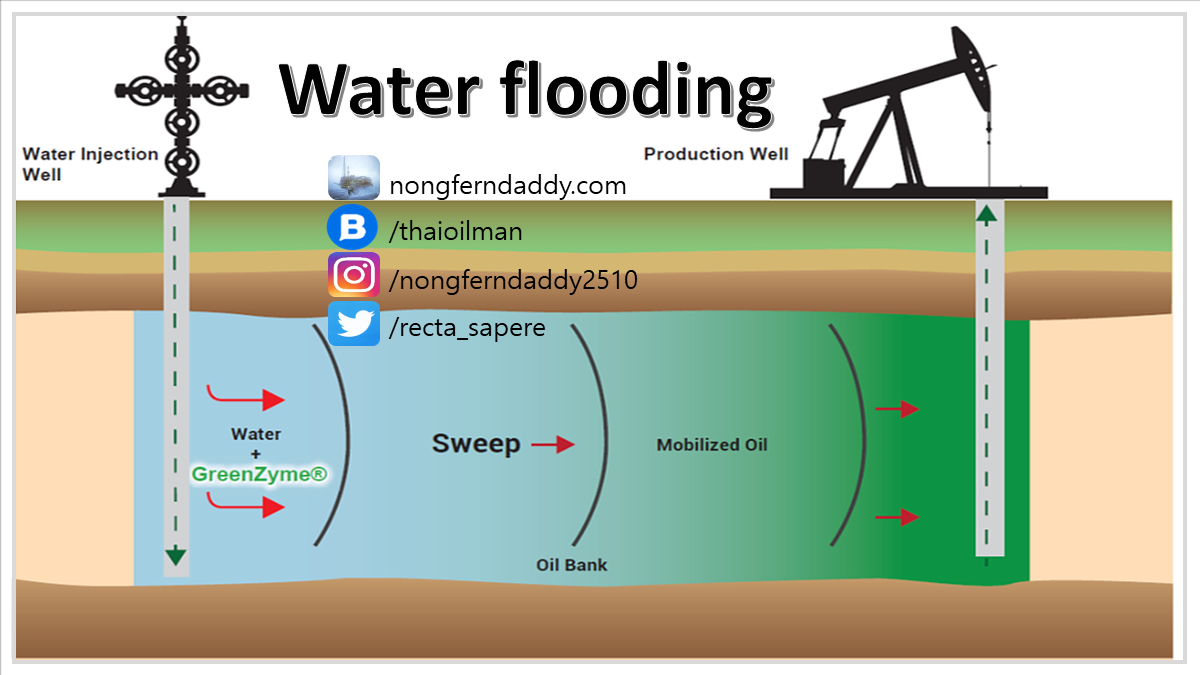
Water flooding เป็นหนึ่งวิธีการทำ Improved Oil Recovery ก่อนที่จะทำ water flooding เราจะมีตัวเลือก 2 ข้อ คือให้น้ำมันไหลขึ้นมาเองโดยใช้แรงดันจากแหล่งกักเก็บ (Natural flow) และ ติดตั้งอุปกรณ์พวก Artificial lift ถ้า 2 ข้อนี้เอาไม่อยู่แล้ว จึงจะทำ Improved Oil Recovery
หลักการของ Water flooding คือ เจาะหลุมเอาไว้สำหรับปั๊มน้ำลงไปในแหล่งกักเก็บ แล้วก็ปั๊มน้ำด้วยแรงดันสูงลงไปในแหล่งกักเก็บ เพื่อให้น้ำที่ปั๊มลงไป ไปแทนที่น้ำมันที่อยู่ในแหล่งกักเก็บนั้น และยังช่วยเพิ่มความดันในแหล่งกักเก็บ (Reservoir pressure) อีกด้วย เมื่อในแหล่งกักเก็บมีความดันเพิ่มขั้น ก็จะช่วยดันให้น้ำมันไหลเข้าไปหลุมผลิตมากกว่าเดิม
อีกเรื่องหนึ่ง ที่บางท่านอาจจะสับสนระหว่าง Water flooding well กับ Disposal well
Disposal well อธิบายได้ว่า ในการผลิตปิโตรเลียม ของไหล (fluid) ที่ขึ้นมาจากหลุมปิโตรเลียม (production well) จะมี แก๊ส, น้ำมัน และน้ำ เมื่อเราแยกทั้ง 3 ส่วนนี้แล้ว แก๊สจะไหลไป burn ที่ flare (ปล่องเผา) น้ำมันจะไหลไปที่ Oil storage tank และน้ำจะไหลไปที่ Water tank ซึ่งน้ำที่อยู่ใน Water tank นี้แหละ ที่เราต้องเอาไปปั๊มกลับลงหลุม หลุมที่ปั๊มน้ำส่วนนี้ลงไป เรียกว่า Disposal well
มีคลิปให้ดูด้วยครับ เพิ่มความเข้าใจ
Waterflooding is the use of water injection to increase the production from oil reservoirs. Use of water to increase oil production is known as “secondary recovery” and typically follows “primary production,” which uses the reservoir’s natural energy (fluid and rock expansion, solution-gas drive, gravity drainage, and aquifer influx) to produce oil.
Rationale for waterflooding
The principal reason for waterflooding an oil reservoir is to increase the oil-production rate and, ultimately, the oil recovery. This is accomplished by “voidage replacement”—injection of water to increase the reservoir pressure to its initial level and maintain it near that pressure. The water displaces oil from the pore spaces, but the efficiency of such displacement depends on many factors (e.g., oil viscosity and rock characteristics). In oil fields such as Wilmington (California, US) and Ekofisk (North Sea), voidage replacement also has been used to mitigate additional surface subsidence. In these cases, the high porosity of the unconsolidated sandstones of the Wilmington oil field’s reservoirs and of the soft chalk reservoir rock in the Ekofisk oil field had compacted significantly when the reservoir pressure was drawn down during primary production.
Over the past 40 years, SPE has published three significant and in-depth books written by Craig,[1] Willhite,[2] and Rose et al.[3] that address waterflooding technology.