Well Control ตอน Concurrent Method – วิธีนี้แรกเริ่มเดิมที ไม่ได้เอารวมไว้ เพราะไม่ค่อยมีใครใช้กัน มันยุ่งยาก และ ใช้จริงให้ได้ผลนั้นยากมากๆ เพราะอะไรเหรอครับ มา …. ตามมา … เราไปดูกัน
ทบทวนก่อนนิดนึง driller method นี่ง่าย พอรู้ว่ามี influx เข้ามา มีน้ำโคลนหนักเท่าไรก็ปั๊มไล่ influx ออกไปก่อน
ส่วน wait and weight พอรู้ว่ามี influx เข้ามา ปิดหลุม รอผสมน้ำโคลนให้ได้น้ำหนักที่คิดว่าเอาอยู่ ผสมน้ำโคลนเสร็จก็ค่อยปั๊ม
Well Control ตอน Concurrent Method
ส่วน concurrent นี้ แปลตรงตัวคือ ทำไปพร้อมๆกัน นั่นคือ พอ influx เข้ามาปุ๊บ ปั๊มเลยไม่รอ ด้วยน้ำโคลนน้ำหนักอะไรก็ตามที่มีอยู่ ระหว่างปั๊มไล่ influx ก็ผสมน้ำโคลนให้หนักจนถึงนน.ที่เอาอยู่ พอได้นน.ที่เอาอยู่ก็ปั๊มลงไป จะเห็นว่ามันยาก คือเอา driller method และ wait and weight มารวมกัน
driller method ง่ายมีน้ำโคลนน้ำหนักเดียวใช้ไล่ influx ขึ้นมาปากบ่อ แล้วใช้น้ำโคลนที่หนักกว่า ปั๊มไล่น้ำโคลนเบาอกไป
Wait and weight ยากขึ้นมานิสนุงเอาน้ำโคลนหนักไล่ทั้งน้ำโคลนเบาและ influx ออกในคราวเดียว
จะเห็นว่า driller method และ wait and weight นั้น เราเริ่มขบวนการไล่ Influx ตอนที่ Influx มันอยู่ก้นหลุม
แต่ concurrent นี้ผมเรียกว่าวิธีใจร้อนก็แล้วกัน influx เข้ามาปั๊บ ปั๊มด้วยน้ำโคลนที่มีอยู่เหมือน driller method แต่ยังไม่ต้องรอจนไล่ influx ถึงปากหลุมแบบ driller method ผสมน้ำโคลนหนักได้ปริมาตรและน้ำหนักที่ต้องการได้เมื่อไรก็ปั๊มลงไปเลย
ผลก็คือ ตอนที่เริ่มปั๊มน้ำโคลนหนัก influx ก็อยู่กลางๆหลุม (ไม่เหมือน wait and weight ที่ตอนเริ่มปั๊มน้ำโคลหนัก influx อยู่ก้นหลุม) influx อยู่ตรงไหนก็ไม่รู้แน่ชัด มีน้ำโคลนเดิม(เบา)ไล่ตูดอยู่ปริมาตรหนึ่ง แล้วก็มีน้ำโคลนใหม่(หนัก)ไล่ตูดน้ำโลนเบาอยู่อีกกระทอก
… เอวังครับ ซับซ้อนเกื้น เวลาทำจริงๆ ไม่รู้ว่าอะไรอยู่ตรงไหน ทำใน excel นะเวิร์ค ง่าย แต่เอาเข้าจริง หุหุ ไม่มีใครเสี่ยงทำครับ
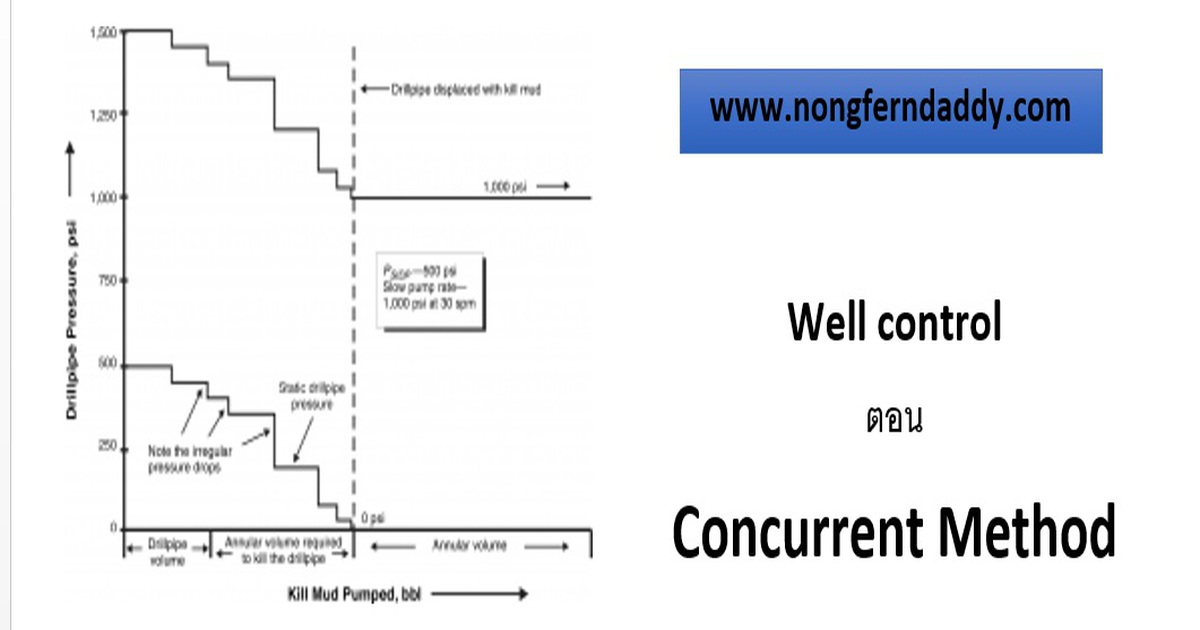
This method is the most difficult to execute properly (see Fig. 3). As soon as the kick is shut in and the pressures are read, pumping immediately begins. The mud density is increased as rapidly as rig facilities will allow. The difficulty is determining the mud density being circulated and its relative position in the drillpipe. Because this position determines the drillpipe pressures, the rate of pressure decrease may not be as consistent as in the other two methods. As a new density arrives at the bit, or a predetermined depth, the drillpipe pressure is decreased by an amount equal to the hydrostatic pressure of the new mud-weight increment. When the drillpipe is displaced with kill mud, the pumping pressure is maintained constant until kill mud reaches the flow line.